Tuesday, March 10, 2015
Documents List API Best Practices Sharing Multiple Documents Using Collections
Google Docs supports sharing collections and their contents with others. This allows multiple Google Docs resources to be shared at once, and for additional resources added to the collection later to be automatically shared.
Class.io, an EDU application on the Google Apps Marketplace, uses this technique. When a professor creates a new course, the application automatically creates a Google Docs collection for that course and shares it with all the students. This gives the students and professor a single place to go in Google Docs to access and manage all of their course files.
A collection is a Google Docs resource that contains other resources, typically behaving like a folder on a file system.
A collection resource is created by making an HTTP POST to the feed link with the category element’s term set to http://schemas.google.com/docs/2007#folder, for example:
<?xml version=1.0 encoding=UTF-8?>
<entry xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom">
<category scheme="http://schemas.google.com/g/2005#kind"
term="http://schemas.google.com/docs/2007#folder"/>
<title>Example Collection</title>
</entry>
To achieve the same thing using the Python client library, use the following code:
from gdata.docs.data import Resource
collection = Resource(folder)
collection.title.text = Example Collection
# client is an Authorized client
collection = client.create_resource(entry)
The new collection returned has a content element indicating the URL to use to add new resources to the collection. Resources are added by making HTTP POST requests to this URL.
<content
src="https://docs.google.com/feeds/default/private/full/folder%3A134acd/contents"
type="application/atom+xml;type=feed" />
This process is simplified in the client libraries. For example, in the Python client library, resources can be added to the new collection by passing the collection into the create_resource method for creating resources, or the move_resource method for moving an existing resource into the collection, like so:
# Create a new resource of document type in the collection
new_resource = Resource(type=document, title=New Document)
client.create_resource(new_resource, collection=collection)
# Move an existing resource
client.move_resource(existing_resource, collection=collection)
Once resources have been added to the collection, the collection can be shared using ACL entries. For example, to add the user user@example.com as a writer to the collection and every resource in the collection, the client creates and adds the ACL entry like so:
from gdata.acl.data import AclScope, AclRole
from gdata.docs.data import AclEntry
acl = AclEntry(
scope = AclScope(value=user@example.com, type=user),
role = AclRole(value=writer)
)
client.add_acl_entry(collection, acl)
The collection and its contents are now shared, and this can be verified in the Google Docs user interface:
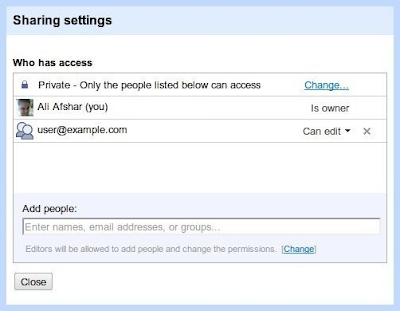
Note: if the application is adding more than one ACL entry, it is recommended to use batching to combine multiple ACL entries into a single request. For more information on this best practice, see the latest blog post on the topic.
The examples shown here are using the raw protocol or the Python client library. The Java client library also supports managing and sharing collections.
For more information on how to use collections, see the Google Documents List API documentation. You can also find assistance in the Google Documents List API forum.
 | Ali Afshar profile | twitter Ali is a Developer Programs engineer at Google, working on Google Docs and the Shopping APIs which help shopping-based applications upload and search shopping content. As an eternal open source advocate, he contributes to a number of open source applications, and is the author of the PIDA Python IDE. Once an intensive care physician, he has a special interest in all aspects of technology for healthcare. |
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.